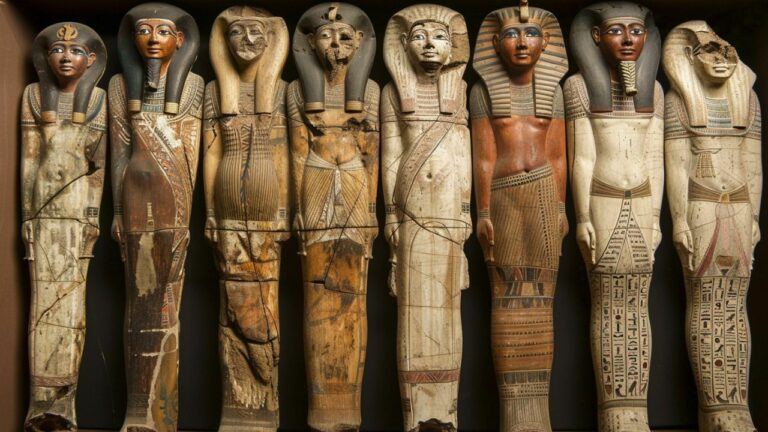
Introduction to the Pharaohs of Ancient Egypt
Did you know that the pharaohs of Ancient Egypt were not just political leaders but also revered religious figures? The word “pharaoh” derived from the term “Great House,” symbolizing the immense power and authority they held over the land and people of Egypt. These mighty rulers played a pivotal role in shaping the ancient Egyptian civilization, leaving behind a legacy that continues to captivate and intrigue us today.
Key Takeaways:
- The pharaohs of Ancient Egypt were both political and religious figures.
- The term “pharaoh” referred to the palace where the ruler resided.
- Pharaohs held immense power and authority, shaping the ancient Egyptian civilization.
- They were revered as the link between the gods and the people.
- The legacy of the pharaohs continues to fascinate and captivate modern society.
The Role and Power of the Pharaohs in Nile River Civilization
As the supreme leaders of ancient Egypt, the pharaohs held both political and religious positions. They acted as mediators between the gods and the people, ensuring religious harmony and performing sacred ceremonies. Moreover, the pharaohs governed the land, making laws, waging war, and collecting taxes. Their power extended to every aspect of Egyptian society, and their decrees were absolute. Through their leadership, the pharaohs shaped and influenced the development of the Nile River civilization, leaving a lasting impact on various aspects of ancient Egyptian culture.
“The pharaohs were not only the rulers of Egypt but also held divine authority as the chosen ones to communicate with the gods. Their command over political, religious, and social matters allowed them to shape the Nile River civilization,” says Dr. Sarah Johnson, an Egyptologist.
A significant aspect of the pharaohs’ power lay in their ability to maintain a delicate balance between the people’s religious beliefs and the practical aspects of governance. They were responsible for ensuring that the gods were appeased through rituals and sacrifices, as it was believed that their favor was essential for the well-being and prosperity of the civilization.
In addition to their religious duties, the pharaohs held absolute authority in matters of legislation, law enforcement, and taxation. They formulated laws that governed the behavior of the society and dealt with matters of justice. The pharaohs also led their armies in times of war, defending the borders of Egypt and expanding its territories.
Furthermore, the pharaohs played a crucial role in the economic development of ancient Egypt. They oversaw the collection of taxes, regulated trade, and were responsible for the construction of monumental structures that served both religious and political purposes.
The influence of the pharaohs reached every corner of the Nile River civilization. Their monumental achievements in architecture, such as the majestic pyramids and temples, stand as a testament to their power and enduring legacy. The art, language, religion, and social structure of ancient Egyptian culture were deeply shaped by the reigns of these eminent rulers.

The pharaohs left an indelible mark on the cultural landscape, ensuring that their place in history would be remembered for centuries to come.
Origins and Evolution of the Pharaoh’s Title Over Millennia
The title of pharaoh and its significance evolved over the course of millennia. The term “pharaoh” originated from the term “great house,” referring to the palace or kingdom of the ruler. Initially, the rulers of ancient Egypt were known as kings. However, with the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt by Narmer, the pharaohs emerged as the lords of two lands. This marked a significant shift in the role and status of the rulers, as they were no longer mere mortal kings but god-kings, with divine authority and connection to the gods.
Etymology of “Pharaoh” and Initial Kingship
The title “pharaoh” finds its roots in the term “great house,” emphasizing the royal palace or kingdom. In the beginning, the rulers of ancient Egypt held the title of kings, serving as the political and religious leaders of their civilization. These early kings were seen as mortal rulers, embodying power and authority on earth.
Unification of Upper and Lower Egypt by Narmer
The unification of Upper and Lower Egypt by Narmer, also known as Menes, marked a pivotal moment in ancient Egyptian history. This unification brought together the lands of Upper and Lower Egypt under one ruler and laid the foundation for the pharaohs’ divine authority. With the consolidation of power, the pharaohs became the symbol of unity and rulers of both realms.

The Shift from Kings to God-Kings
As the pharaohs ascended to power, they transitioned from mortal kings to god-kings, possessing divine authority and connection to the gods. The pharaohs were believed to be the living embodiment of the gods on Earth, ensuring religious harmony and carrying out sacred ceremonies. This shift in perception elevated the pharaohs’ status and solidified their role as the ultimate rulers of ancient Egypt.
Iconic Pharaohs and Their Contributions to Ancient Egyptian Culture
Throughout the history of ancient Egypt, there were numerous iconic pharaohs who left a lasting legacy through their rule and achievements. These pharaohs made significant contributions to the culture of their civilization, shaping the artistic, architectural, and political landscape of ancient Egypt.
One such pharaoh is Akhenaten, known for his religious reforms that introduced the concept of monotheism and the worship of the sun disc, Aten. Tutankhamun, popularly known as King Tut, is another renowned pharaoh who ascended the throne at a young age and ruled during the period of the New Kingdom. His tomb, discovered in 1922, unveiled a treasure trove of artifacts, providing valuable insights into ancient Egyptian burial practices.

Hatshepsut, the first female pharaoh of ancient Egypt, was admired for her prosperous reign and ambitious building projects, including the magnificent Mortuary Temple of Hatshepsut. Amenhotep III, celebrated for his grand construction projects and diplomatic alliances, further contributed to the flourishing of ancient Egyptian culture.
Ramses II, also known as Ramses the Great, is renowned for his military conquests and the architectural marvels he left behind, including the Abu Simbel Temples and the Temple of Karnak. Cleopatra VII, the last pharaoh of ancient Egypt, played a significant role in the history of Egypt and the Roman Empire, known for her political prowess and alliances.
These iconic pharaohs not only brought about religious reforms and monumental construction projects but also fostered diplomatic relations and military advancements. Their contributions and achievements continue to awe and inspire people, ensuring that the rich history and cultural heritage of ancient Egypt are celebrated for generations to come.
Architectural Marvels: The Pyramids of Egypt and Pharaonic Monuments
One of the most awe-inspiring legacies of the pharaohs is the grandeur of the Egyptian pyramids and other pharaonic monuments. These architectural marvels stand as a testament to the advanced engineering skills and cultural significance of ancient Egypt.
Rationale Behind Constructing the Grand Pyramids
The construction of the pyramids served multiple purposes, with the most prominent being tombs for the pharaohs. These monumental structures were meant to house the bodies of the pharaohs and ensure their eternal rest. The pyramids were also built as a representation of the pharaohs’ eternal power and authority, showcasing the might and majesty of ancient Egypt.
Symbolism of Mortuary Temples and Royal Tombs
In addition to the pyramids, ancient Egypt is renowned for its mortuary temples and royal tombs. These structures held immense religious and symbolic value, serving as places of worship and rituals dedicated to the pharaohs. The mortuary temples emphasized the pharaohs’ connection to the gods and their role as divine rulers. The royal tombs were meticulously designed to guide the pharaohs’ journey into the afterlife, providing them with the necessary provisions and treasures for their eternal existence.
Discoveries from Pharaohs’ Tombs and What They Reveal
Explorations and excavations of pharaohs’ tombs have yielded remarkable discoveries that shed light on ancient Egyptian society. Treasures, artifacts, and intricate murals found within these tombs provide valuable insights into the religious beliefs, daily life, and artistic expressions of the ancient Egyptians. These discoveries continue to deepen our understanding of the pharaohs’ culture and the fascinating civilization they ruled over.
Conclusion
The pharaohs of ancient Egypt have left an enduring legacy that continues to captivate modern society. Their monumental architectural achievements, religious practices, and political influence have shaped the course of history and have fascinated people for centuries.
The allure of ancient Egypt and its pharaohs is evident in the ongoing discoveries and research conducted by archaeologists and historians. With each new excavation and exploration, more secrets of the pharaohs and their civilization are unveiled, fueling the intrigue and fascination surrounding their enigmatic world.
From the awe-inspiring pyramids to the intricate hieroglyphs, the ancient Egyptian civilization has left an indelible mark on the world. The pharaohs’ influence can be seen not only in the rich cultural heritage they left behind but also in the modern fascination with their reigns and the ongoing efforts to uncover their hidden treasures.
As technology and archaeological techniques continue to advance, there is no doubt that the study of ancient Egypt and its pharaohs will yield even more discoveries and insights. The enduring legacy of the pharaohs lives on, captivating the imagination of people around the world and inspiring a deeper understanding of one of history’s most remarkable civilizations.
FAQ
Who were the pharaohs of Ancient Egypt?
The pharaohs of Ancient Egypt were the political and religious leaders of their society.
What does the word “pharaoh” mean?
The word “pharaoh” derives from the term “Great House,” which referred to the palace where the pharaoh resided.
What role did the pharaohs play in ancient Egyptian civilization?
The pharaohs held immense power and authority, ruling over the land of Egypt and its people. They shaped the ancient Egyptian civilization, leaving behind a remarkable legacy.
What were the responsibilities of the pharaohs?
The pharaohs acted as mediators between the gods and the people, ensuring religious harmony and performing sacred ceremonies. They also governed the land, making laws, waging war, and collecting taxes.
How did the title of pharaoh evolve over time?
Initially, the rulers of ancient Egypt were known as kings. However, with the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt, the pharaohs emerged as god-kings with divine authority and connection to the gods.
Who were some famous pharaohs in ancient Egypt?
Some iconic pharaohs include Akhenaten, Tutankhamun, Hatshepsut, Amenhotep III, Ramses II, and Cleopatra VII. They made significant contributions to the culture of their civilization.
What is the significance of the Egyptian pyramids?
The pyramids served as tombs for the pharaohs, symbolizing their eternal power and authority. They also held significant religious and symbolic value.
What have archaeologists discovered in the pharaohs’ tombs?
Explorations and excavations of the pharaohs’ tombs have provided valuable insights into ancient Egyptian society, revealing treasures and artifacts.
What is the enduring legacy of the pharaohs?
The pharaohs have left a lasting impact on the history, art, architecture, and political landscape of ancient Egypt. Their legacy continues to captivate and intrigue modern society.
Why is there ongoing fascination with ancient Egypt’s pharaohs?
The ongoing discoveries and research conducted by archaeologists and historians fuel the intrigue and fascination with ancient Egypt and its pharaohs.